Rigid Flex Board
A rigid flex board is a hybrid circuit that combines elements of both rigid and flexible PCBs to create a design that can be folded, bent, or twisted without affecting its functionality. Rigid flex boards are used in high-reliability, high-density applications where space and weight are critical factors, including aerospace and medical devices.
In addition to their durability, rigid flex boards offer other advantages that make them a smart choice for electronic designers and manufacturers. They can help reduce assembly costs by reducing the need for connectors and cables. They can also increase component density for more compact designs. Rigid flex circuits also have a greater lifespan than rigid or flex circuit boards, making them an ideal choice for applications in harsh environments.
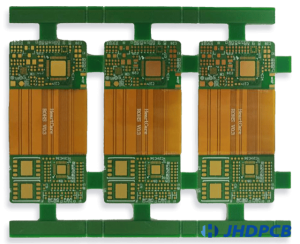
The hybrid nature of rigid flex board allows them to bend and fold to fit into tight or irregularly-shaped spaces, saving valuable space in electronic assemblies. This feature makes them an ideal choice for miniaturized electronics, such as smartphones and tablets, where space is a premium. Additionally, rigid flex circuits can be designed in three dimensions, allowing engineers to use more advanced, intricate designs.
What Is a Rigid Flex Board?
One of the biggest disadvantages of rigid flex circuits is that they can be more susceptible to damage from vibration and shock. However, this can be mitigated by implementing certain design and manufacturing considerations. For example, using materials with a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), implementing thermal management techniques like heat sinks, and optimizing trace widths, thicknesses, and copper plane configurations can all improve rigid flex circuit board reliability and longevity.
Rigid flex circuit boards can also be modified to reduce their susceptibility to vibration and shock by adding stiffeners. These are thin sheets of rigid material added to selected areas of a flex circuit board. They add mechanical stability to the flex sections and prevent them from warping or cracking under stress. Another way to minimize vibration and shock is by adding a layer of metal, such as stainless steel or aluminum, to the rigid section of the board.
Rigid-flex boards represent a remarkable innovation in the realm of electronic circuit design and manufacturing. These boards seamlessly integrate the flexibility of flexible circuits with the structural stability of rigid boards, offering unique advantages in various applications ranging from aerospace and military systems to consumer electronics and medical devices. The convergence of flexibility and rigidity in a single board structure opens up new avenues for creating compact, lightweight, and durable electronic devices.
Although the process of manufacturing a rigid flex circuit is more complex than other types of printed circuit boards, the long-term benefits make it well worth the extra time and expense. If you’re interested in incorporating rigid flex technology into your next project, be sure to talk to an expert about design options and manufacturing processes. A trusted PCB manufacturer will have the experience, equipment, and knowledge to produce a robust, reliable rigid flex circuit that’s perfectly suited for your application.